Quick Install Baetyl¶
Compared to manually download software in previous version, it supports installing Baetyl through package manager in newer version. With this method, you can quickly install Baetyl by simply typing a few commands at terminal.
Installation packages are provided for Ubuntu16.04, Ubuntu18.04, Debian9, CentOS7 and Raspbian-stretch currently. The supported platforms are amd64, i386, armv7l, and arm64.
Baetyl supports two running modes: docker container mode and native process mode. This document will be described in docker container mode.
Install Docker¶
Baetyl relies on Docker Engine in docker container mode. You can install Docker (for Linux-like systems) with the following command if it’s not installed yet:
curl -sSL https://get.docker.com | sh
View the version of installed Docker:
docker version
NOTE: According to the Official Release Log, the version of Docker lower than 18.09.2 has some security implications. It is recommended to install/update the Docker to 18.09.2 and above.
For more details, please see the official documentation.
Install Baetyl¶
The rpm and deb packages will be released accordingly when Baetyl releases a new version. You can install Baetyl to the device through package manager with following command:
curl -sSL http://dl.baetyl.io/install.sh | sudo -E bash -
If everything is ok, Baetyl will be installed on the /usr/local directory after the execution is complete.
Import the example configuration (optional)¶
As an edge computing framework, Baetyl provides MQTT connect service through hub module, provides local functional service through function manager module and some runtime modules like python27, python36, nodejs85, sql and so on. What’s more, all the modules are started by Baetyl master through a configuration file. More detailed contents about the module’s configuration please refer to Configuration Interpretation for further information.
Baetyl officially provides an example configuration for some module which can be imported using following command:
curl -sSL http://dl.baetyl.io/install_with_docker_example.sh | sudo -E bash -
The example configuration is for learning and testing purposes only. You should perform on-demand configuration according to actual working scenarios.
There is no need to import any configuration files if no modules need to launch.
Start Baetyl¶
The newer version of Baetyl uses Systemd as a daemon, and you can start Baetyl with the following command:
sudo systemctl start baetyl
If you have previously installed Baetyl or imported a new configuration file, it is recommended to use the reboot method:
sudo systemctl restart baetyl
Stop Baetyl:
sudo systemctl stop baetyl
If you only want to run Baetyl in the foreground, execute the following command::
sudo baetyl start
Verify successful installation¶
After installation, you can verify whether Baetyl is successfully installed or not by the following steps:
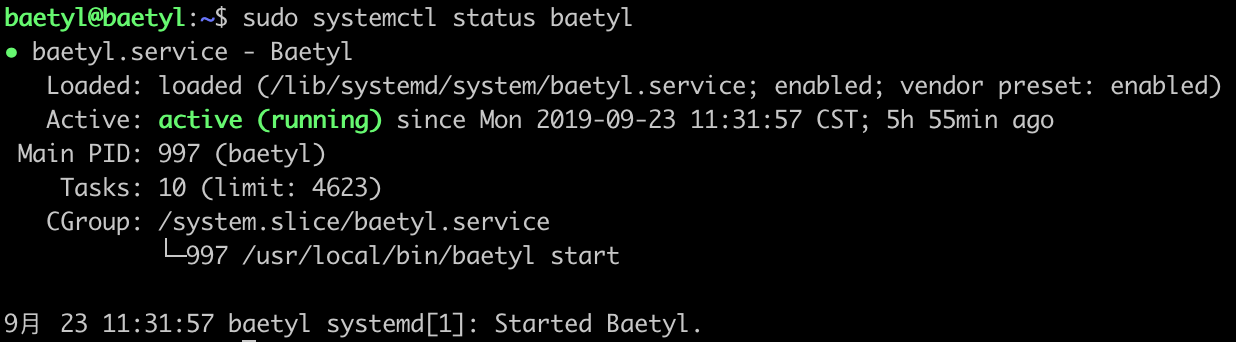
- executing the command
sudo systemctl status baetylto check whetherbaetylis running, as shown below. Otherwise,baetylfails to start.
 Baetyl
Baetyl
- Executing the command
docker statsto view the running status of Docker containers. Since the Baetyl master will first pull required images from Docker mirror repository, it will take 2~5 minutes to see the baetyl starts successfully. Take the example configurations as above, the running status of containers are as shown below. If some containers are missing, it means they failed to start.
 docker stats
docker stats
- Under the condition of two above failures, you need to view the log of the Baetyl master. And the log file which is stored in /usr/local/var/log/baetyl/baetyl.log by default. Once found errors in the log file, you can refer to FAQ. If necessary, just Submit an issue.