Message Synchronize between baetyl-hub and Baidu IoTHub via Remote Service¶
Statement
- The operating system used in this test is Ubuntu 18.04
- The Baetyl and example configuration should be installed firstly, refer to Quick Install
- The MQTT client toolkit which is used to connect to Baidu IoTHub is MQTT.fx
- The MQTT client toolkit which is used to connect to baetyl-hub is MQTTBox
- The Remote Hub used in this test is Baidu IoTHub
The baetyl-remote-mqtt service was developed to meet the needs of the IoT scenario. The Baetyl(via baetyl-hub service) can synchronize message with remote hub, such as Baidu IoTHub via the baetyl-remote-mqtt service. That is to say, through the baetyl-remote-mqtt service, we can either subscribe the message from Remote Hub and publish it to the baetyl-hub service or subscribe the message from baetyl-hub service and publish it to remote hub platform. The configuration of baetyl-remote-mqtt service can refer to Remote service configuration.
Workflow¶
- Step 1: Create device(MQTT client) connection info(include
endpoint,user,principal,policy, etc.) via Baidu IoTHub. - Step 2: Select MQTT.fx as the MQTT client that used to connect to Baidu IoTHub.
- If connect successfully, then do the following next.
- If connect unsuccessfully, then retry it until it connect successfully. More detailed contents can refer to Connect to Baidu IoTHub with MQTT.fx。
- Step 3: Startup Baetyl in docker container mode, and observe the log of Baetyl.
- If the baetyl-hub service and baetyl-remote-mqtt service start successfully, then do the following next.
- If the baetyl-hub service and baetyl-remote-mqtt service start unsuccessfully, then retry
Step 3until they start successfully.
- Step 4: Select MQTTBox as the MQTT client that connect to BAETYL framework, more detailed contents please refer to Device connect to Hub Service.
- If connect successfully, then do the following next.
- If connect unsuccessfully, then retry
Step 4until it connect successfully.
- Step 5: Due to the configuration of baetyl-remote-mqtt service, using MQTTBox publish message to the specified topic, and observing the receiving message via MQTT.fx. Similarly, using MQTT.fx publish message to the specified topic, and observing the receiving message via MQTTBox.
- Step 6: If both parties in
Step 5can receive the message content posted by the other one, it indicates the Remote function test passes smoothly.
The workflow diagram are as follows.
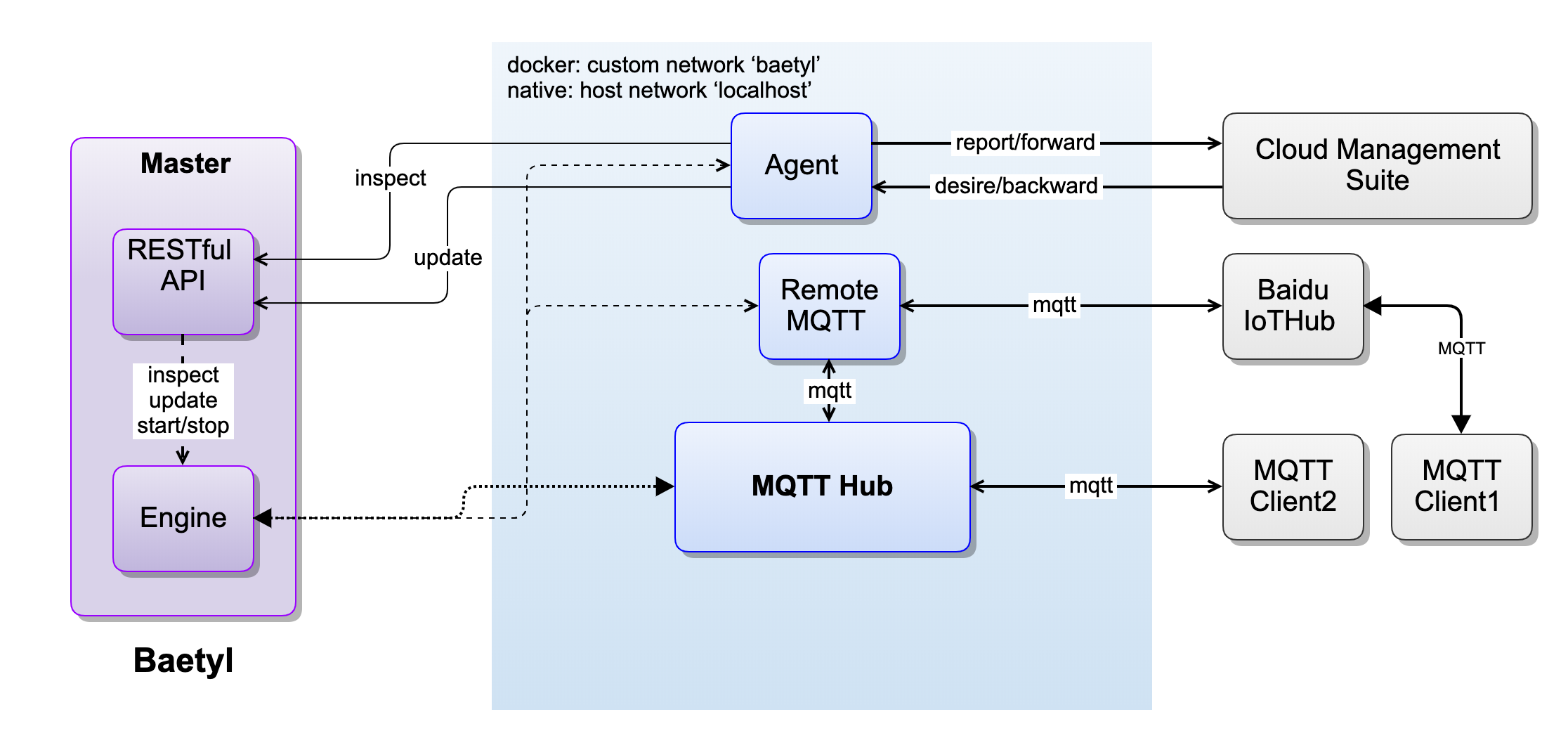 using baetyl-remote-mqtt service to synchronize message
using baetyl-remote-mqtt service to synchronize message
Message Synchronize via baetyl-remote-mqtt service¶
The application configuration in var/db/baetyl/application.yml are as follows:
version: v0
services:
- name: localhub
image: hub.baidubce.com/baetyl/baetyl-hub:latest
replica: 1
ports:
- 1883:1883
mounts:
- name: localhub-conf
path: etc/baetyl
readonly: true
- name: localhub-data
path: var/db/baetyl/data
- name: localhub-log
path: var/log/baetyl
- name: remote-iothub
image: hub.baidubce.com/baetyl/baetyl-remote-mqtt:latest
replica: 1
mounts:
- name: remote-iothub-conf
path: etc/baetyl
readonly: true
- name: remote-iothub-cert
path: var/db/baetyl/cert
readonly: true
- name: remote-iothub-log
path: var/log/baetyl
volumes:
# hub
- name: localhub-conf
path: var/db/baetyl/localhub-conf
- name: localhub-data
path: var/db/baetyl/localhub-data
- name: localhub-log
path: var/db/baetyl/localhub-log
# remote mqtt
- name: remote-iothub-conf
path: var/db/baetyl/remote-iothub-conf
- name: remote-iothub-cert
path: var/db/baetyl/remote-iothub-cert
- name: remote-iothub-log
path: var/db/baetyl/remote-iothub-log
Configuration file location for baetyl-hub service is: var/db/baetyl/localhub-conf/service.yml.
The configuration of baetyl-hub service is as follow:
listen:
- tcp://0.0.0.0:1883
principals:
- username: test
password: hahaha
permissions:
- action: 'pub'
permit: ['#']
- action: 'sub'
permit: ['#']
logger:
path: var/log/baetyl/localhub-service.log
level: "debug"
Configuration file location for baetyl-remote-mqtt service is: var/db/baetyl/remote-iothub-conf/service.yml.
The configuration of baetyl-remote-mqtt service is as follow:
name: remote-iothub
hub:
address: tcp://localhub:1883
username: test
password: hahaha
remotes:
- name: iothub
address: '<iothub_endpoint>' # copy the ssl address from Baidu IoTHub endpoint list, then replace <iothub_endpoint>, such as ssl://xxxxxx.mqtt.iot.gz.baidubce.com:1884, and the xxxxxx represents for endpoint name.
clientid: remote-iothub-1
username: '<username>' # copy the username which supports ssl connect authentication from the above(address) endpoint's user list, such as xxxxxx/test, and the xxxxxx represents for endpoint name.
ca: var/db/baetyl/cert/ca.pem
cert: var/db/baetyl/cert/client.pem
key: var/db/baetyl/cert/client.key
rules:
- hub:
subscriptions:
- topic: t1
remote:
name: iothub
subscriptions:
- topic: t2
qos: 1
logger:
path: var/log/baetyl/remote-service.log
level: 'debug'
According to the configuration of the above, it means that the baetyl-remote-mqtt service subscribes the topic t1 from the baetyl-hub service, subscribes the topic t2 from Baidu IoTHub. When MQTTBox publishes a message to the topic t1, the baetyl-hub service will receive this message and forward it to Baidu IoTHub via baetyl-remote-mqtt service, and MQTT.fx will also receive this message(suppose MQTT.fx has already subscribed the topic t1 before) from Baidu IoTHub. Similarly, When we use MQTT.fx to publish a message to the topic t2, then Baidu IoTHub will receive it and forward it to the baetyl-hub service via baetyl-remote-mqtt service. Finally, MQTTBox will receive this message(suppose MQTTBox has already subscribed the topic t2 before).
In a word, from MQTTBox publishes a message to the topic t1, to MQTT.fx receives the message, the routing path of the message are as follows.
MQTTBox -> baetyl-hub service -> baetyl-remote-mqtt service -> Baidu IoTHub -> MQTT.fx
Similarly, from MQTT.fx publishes a message to the topic t2, to MQTTBox receives the message, the routing path of the message are as follows.
MQTT.fx -> Baidu IoTHub -> baetyl-remote-mqtt service -> baetyl-hub service -> MQTTBox
Establish a Connection between MQTT.fx and Baidu IoTHub¶
As described in Step 1, Step 2, the detailed contents of the connection between MQTT.fx and Baidu IoTHub are as follows.
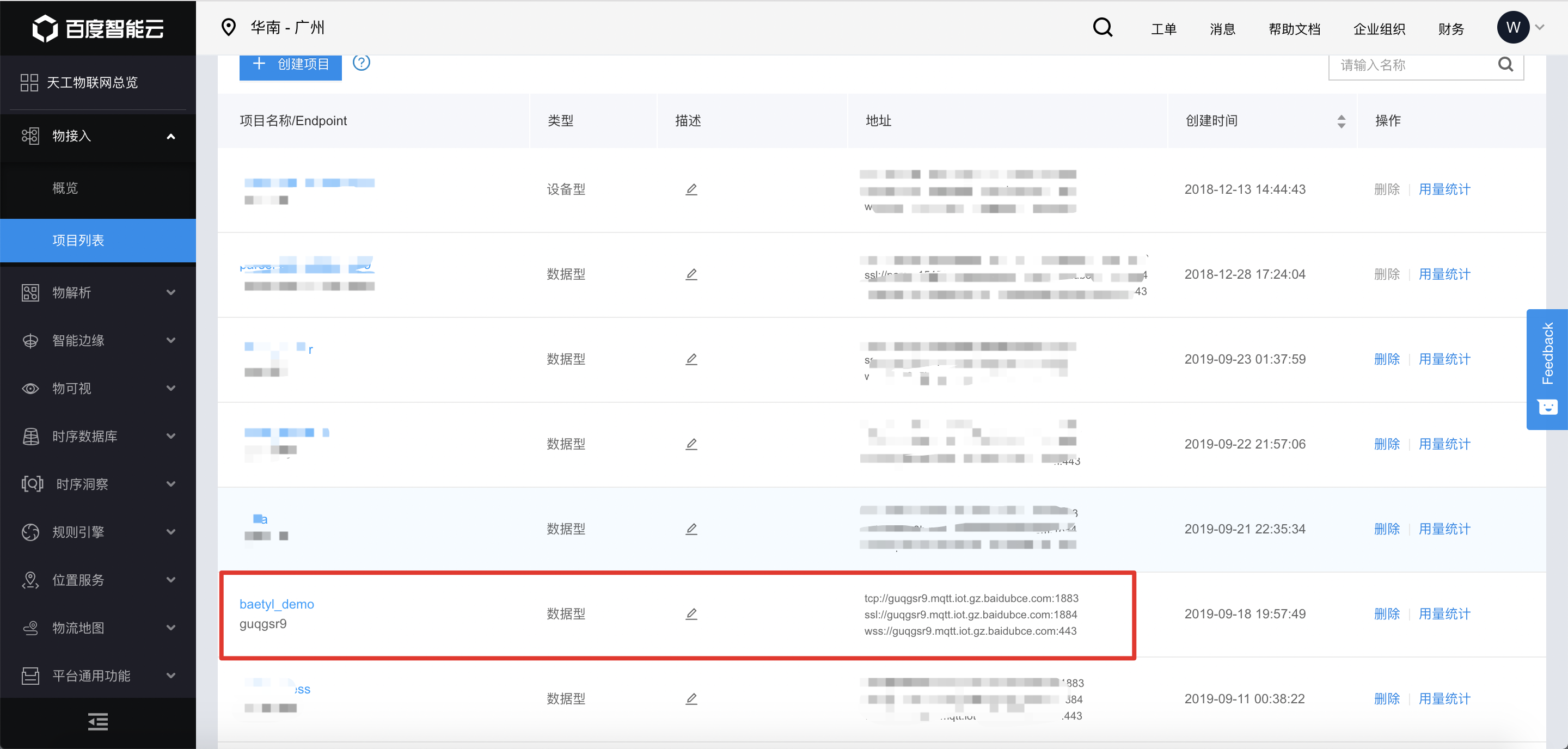 Create endpoint via Baidu IoTHub
Create endpoint via Baidu IoTHub
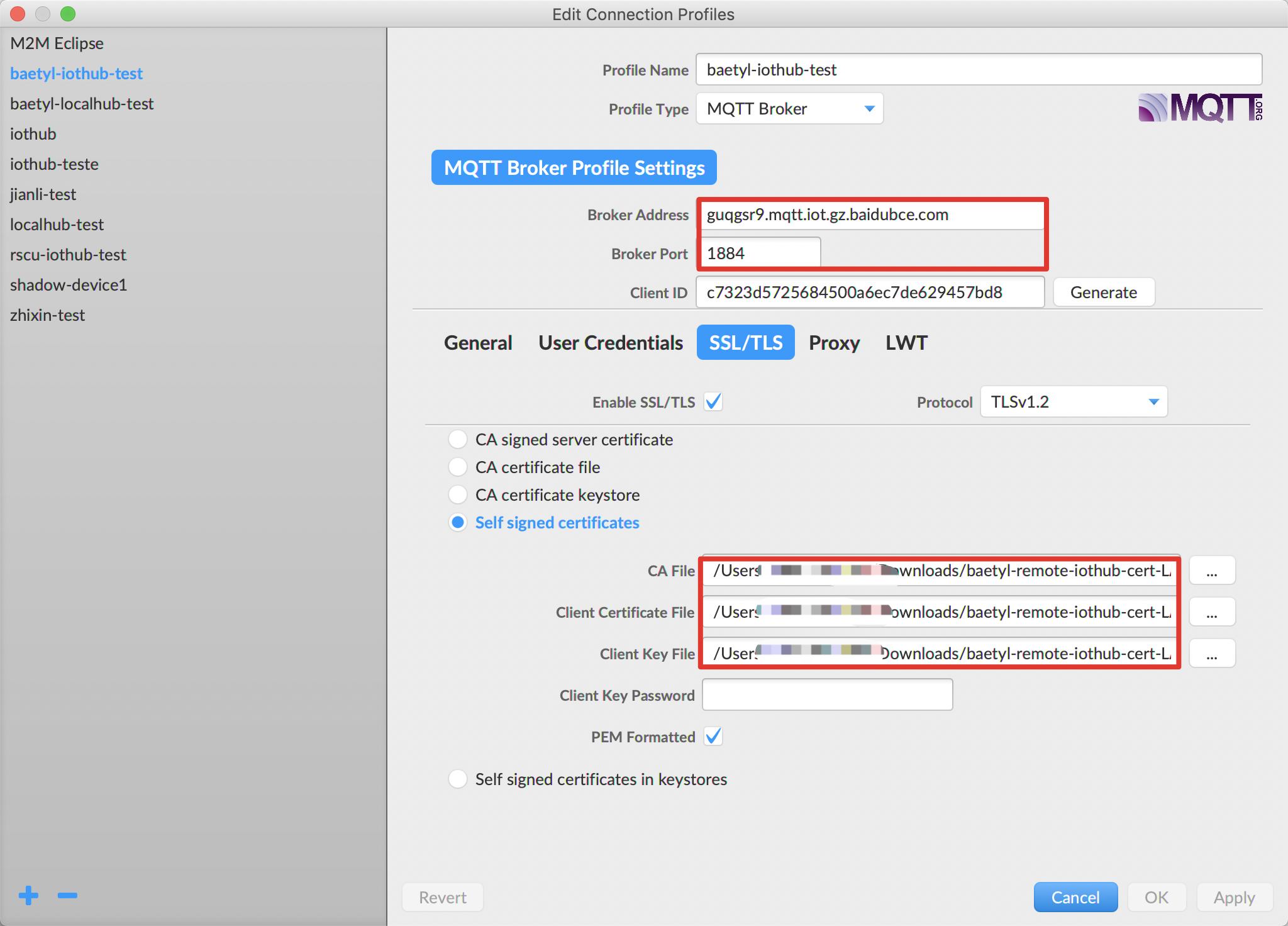 Configuration of MQTT.fx
Configuration of MQTT.fx
After set the configuration of MQTT.fx, click OK or Apply button, then click Connect button, and wait for the connecting. Also, we can check if the connection status is OK via the color button. When the button’s color change to Green, that is to say, the connection is established. Then switch to the Subscribe page and subscribe the topic t1. More detailed contents are shown below.
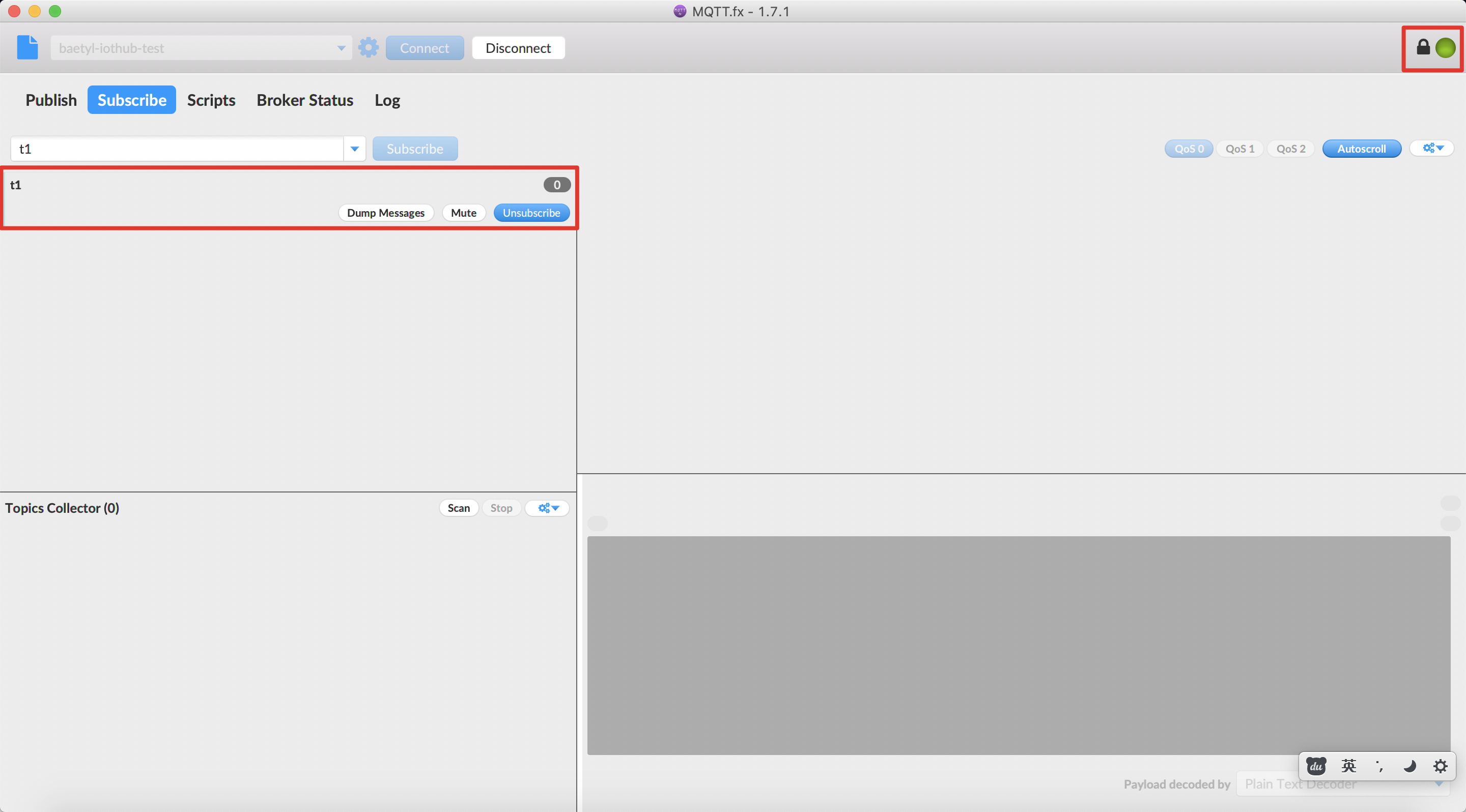 Successfully establish a connection between MQTT.fx and Baidu IoTHub
Successfully establish a connection between MQTT.fx and Baidu IoTHub
Establish a Connection between MQTTBox and the baetyl-hub service¶
As described in Step 3, the baetyl-hub service and baetyl-remote-mqtt service also loaded when Baetyl started. Also, we can lookup the running status of Baetyl through the command sudo systemctl status baetyl.
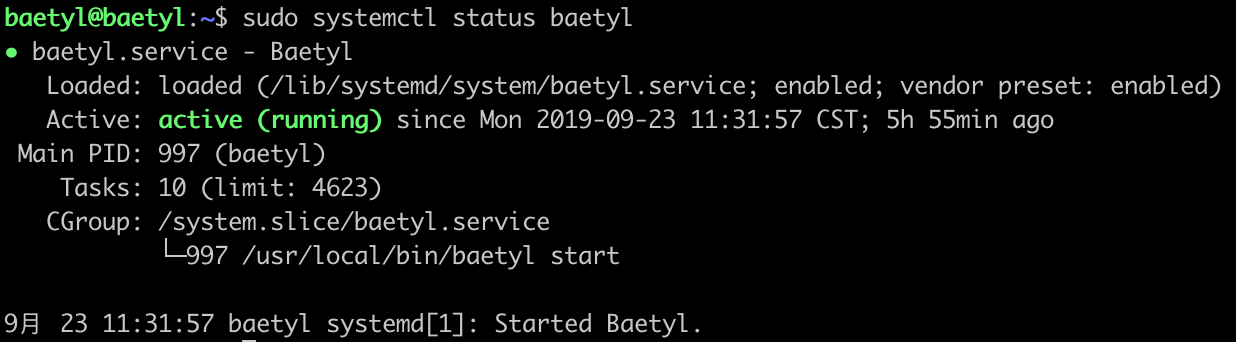 lookup the running status of Baetyl
lookup the running status of Baetyl
In addition, we can execute the command docker stats to view the list of docker containers currently running on the system.
 View the list of docker containers currently running
View the list of docker containers currently running
After Baetyl successfully startup, set the configuration of connection, then establish the connection with the baetyl-hub service and subscribe the topic t2.
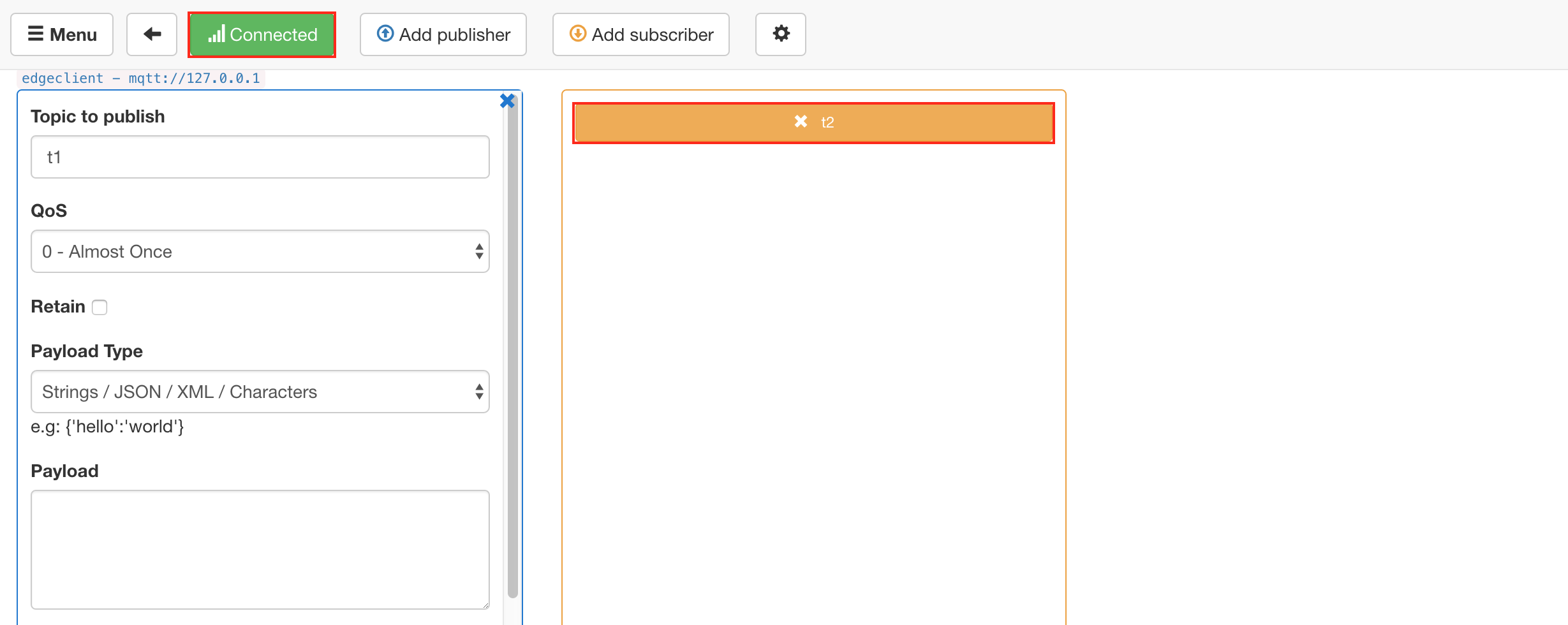 MQTTBox successfully subscribe the topic t2
MQTTBox successfully subscribe the topic t2
Message Synchronize Test¶
Here, MQTT.fx and MQTTBox will be used as message publishers, and the other one will be used as a message receiver.
MQTT.fx publishes message, and MQTTBox receives message
Firstly, using MQTT.fx publishes a message This message is from MQTT.fx. to the topic t2.
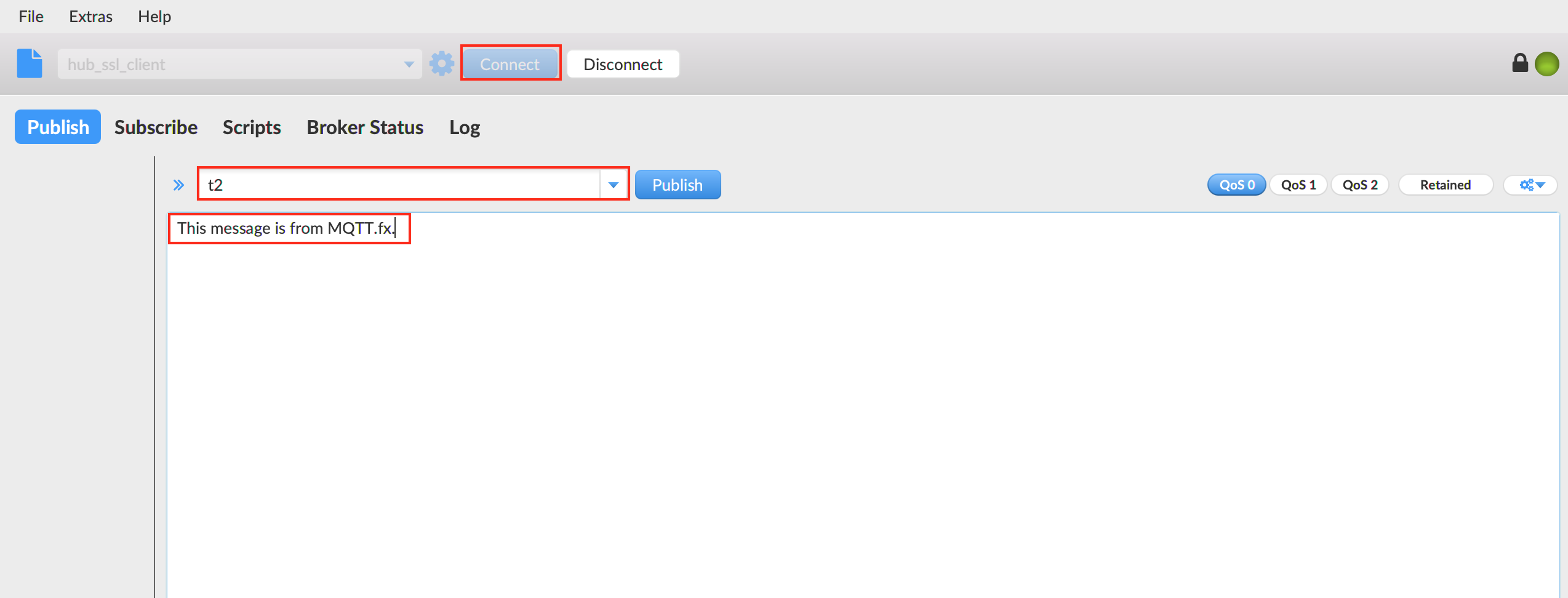 Publishing a message to the topic t2 via MQTT.fx
Publishing a message to the topic t2 via MQTT.fx
At the same time, observing the message receiving status of MQTTBox via the topic t2.
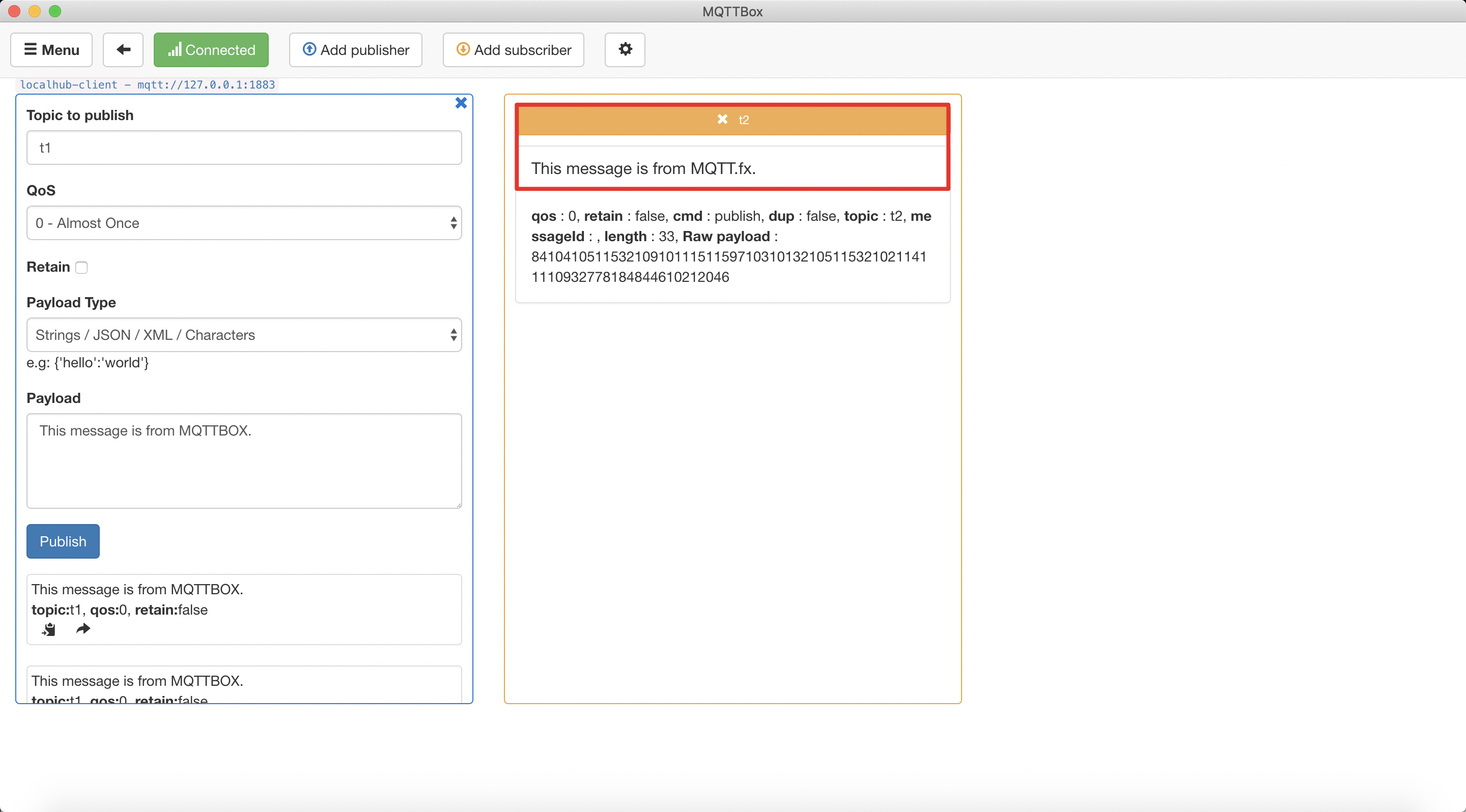 MQTTBox successfully received the message
MQTTBox successfully received the message
MQTTBox publishes message, and MQTT.fx receives message
Similarly, publishing the message This message is from MQTTBox. to the topic t1 via MQTTBox.
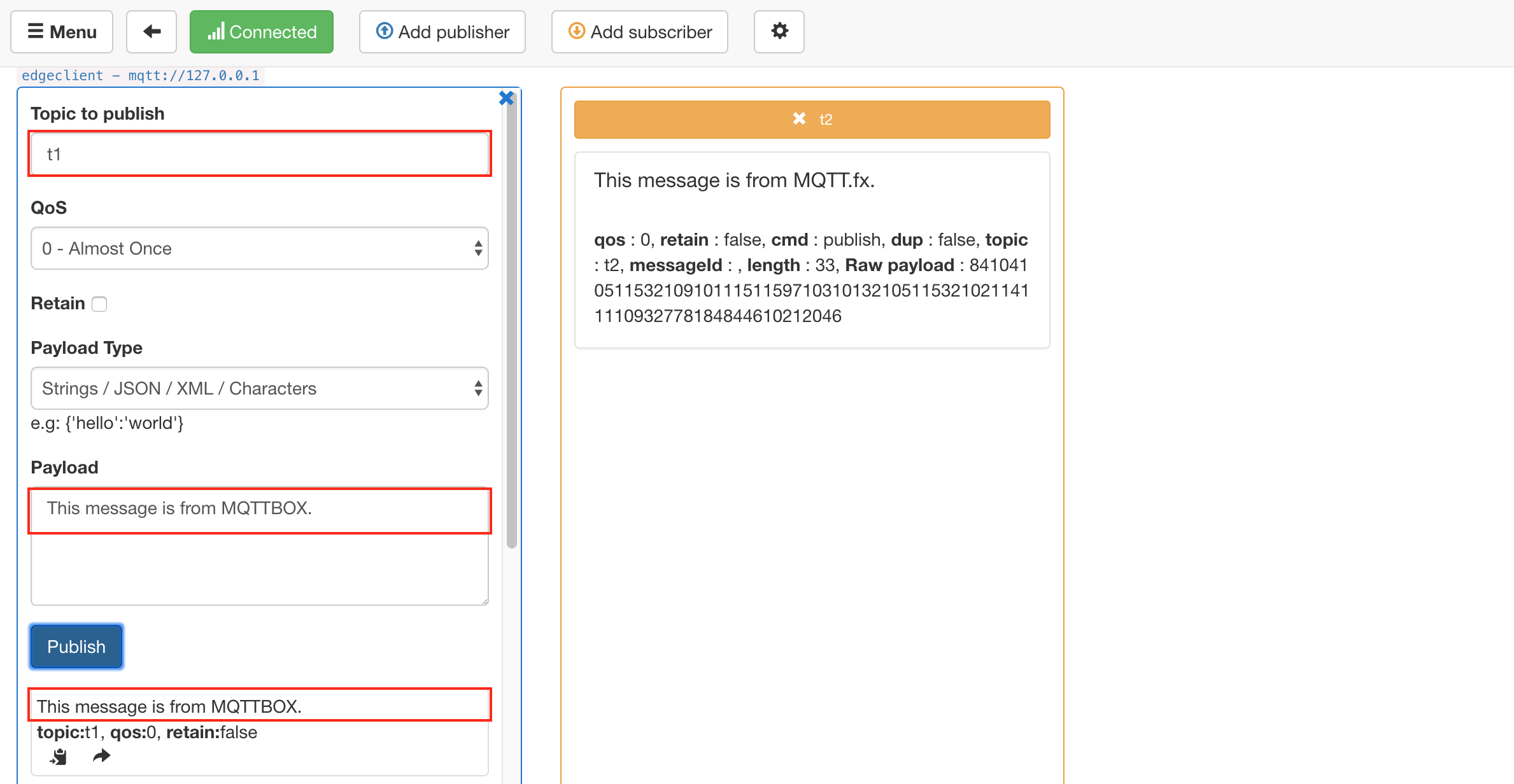 Publishing a message to the topic t1 via MQTTBox
Publishing a message to the topic t1 via MQTTBox
Then we can observe the message receiving status of MQTT.fx via the topic t1.
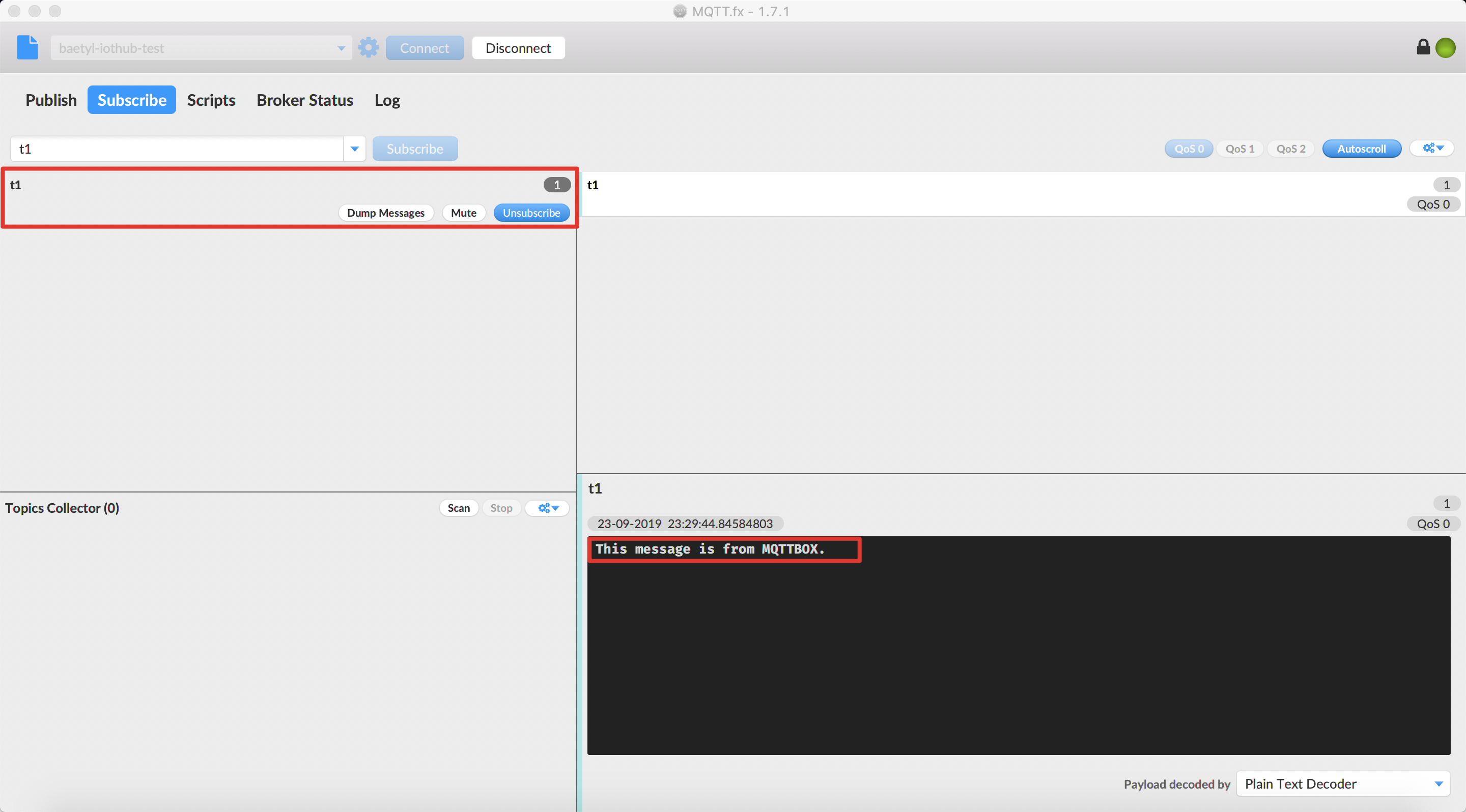 MQTT.fx successfully received the message
MQTT.fx successfully received the message
In summary, both MQTT.fx and MQTTBox have correctly received the specified message, and the content is consistent.