How to write a python script for Python runtime¶
Statement
- The operating system as mentioned in this document is Ubuntu16.04.
- The version of runtime is Python3.6, and for Python2.7, configuration is the same except for the language difference when coding the scripts
- The MQTT client toolkit as mentioned in this document is MQTTBox.
- In this article, the service created based on the Hub module is called
localhubservice. And for the test case mentioned here, thelocalhubservice, function calculation service, and other services are configured as follows:
# The configuration of Local Hub service
# Configuration file location is: `var/db/baetyl/localhub-conf/service.yml`.
listen:
- tcp://0.0.0.0:1883
principals:
- username: 'test'
password: 'hahaha'
permissions:
- action: 'pub'
permit: ['#']
- action: 'sub'
permit: ['#']
# The configuration of Local Function Manager service
# Configuration file location is: var/db/baetyl/function-manager-conf/service.yml
hub:
address: tcp://localhub:1883
username: test
password: hahaha
rules:
- clientid: localfunc-1
subscribe:
topic: py
function:
name: sayhi3
publish:
topic: py/hi
functions:
- name: sayhi3
service: function-sayhi3
instance:
min: 0
max: 10
idletime: 1m
# The configuration of python function runtime
# Configuration file location is: var/db/baetyl/function-sayhi-conf/service.yml
functions:
- name: 'sayhi3'
handler: 'sayhi.handler'
codedir: 'var/db/baetyl/function-sayhi'
# The configuration of application.yml
# Configuration file location is: var/db/baetyl/application.yml
version: v0
services:
- name: localhub
image: hub.baidubce.com/baetyl/baetyl-hub
replica: 1
ports:
- 1883:1883
mounts:
- name: localhub-conf
path: etc/baetyl
readonly: true
- name: localhub-data
path: var/db/baetyl/data
- name: localhub-log
path: var/log/baetyl
- name: function-manager
image: hub.baidubce.com/baetyl/baetyl-function-manager
replica: 1
mounts:
- name: function-manager-conf
path: etc/baetyl
readonly: true
- name: function-manager-log
path: var/log/baetyl
- name: function-sayhi3
image: hub.baidubce.com/baetyl/baetyl-function-python36
replica: 0
mounts:
- name: function-sayhi-conf
path: etc/baetyl
readonly: true
- name: function-sayhi-code
path: var/db/baetyl/function-sayhi
readonly: true
volumes:
# hub
- name: localhub-conf
path: var/db/baetyl/localhub-conf
- name: localhub-data
path: var/db/baetyl/localhub-data
- name: localhub-log
path: var/db/baetyl/localhub-log
# function manager
- name: function-manager-conf
path: var/db/baetyl/function-manager-conf
- name: function-manager-log
path: var/db/baetyl/function-manager-log
# function python runtime sayhi
- name: function-sayhi-conf
path: var/db/baetyl/function-sayhi-conf
- name: function-sayhi-code
path: var/db/baetyl/function-sayhi-code
Baetyl officially provides the Python runtime to load python scripts written by users. The following description is about the name of the python script, the execution function name, input, output parameters, and so on.
Function Name Convention¶
The name of a python script can refer to Python’s universal naming convention, which Baetyl does not specifically limit. If you want to apply a python script to handle an MQTT message, the configuration of Python3.6 runtime service is as follows:
functions:
- name: 'sayhi3'
handler: 'sayhi.handler'
codedir: 'var/db/baetyl/function-sayhi'
Here, we focus on the handler attribute, where sayhi represents the script name and the handler represents the entry function called in the file.
function-sayhi-code/
├── __init__.py
└── sayhi.py
More detailed configuration of Python runtime, please refer to Python runtime configuration.
Parameter Convention¶
def handler(event, context):
# do something
return event
The Python runtime provided by Baetyl supports two parameters: event and context, which are described separately below.
- event: Depend on the
Payloadin the MQTT message- If the original
Payloadis a json format data, then pass in the data handled byjson.loads(Payload) - If the original
Payloadis Byte, string(not Json), then pass in the originalPayload。
- If the original
- context: MQTT message context
- context.messageQOS // MQTT QoS
- context.messageTopic // MQTT Topic
- context.functionName // MQTT functionName
- context.functionInvokeID //MQTT function invokeID
- context.invokeid // as above, be used to compatible with CFC
NOTE: When testing in the cloud CFC, please don’t use the context defined by Baetyl directly. The recommended method is to first determine whether the field is exists or not in the context. If exists, read it.
Hello World¶
Now we will implement a simple python script with the goal of appending a hello world message to each MQTT message. For a dictionary format message, return it directly, and for an none dictionary format message, convert it to string and return.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def handler(event, context):
result = {}
if isinstance(event, dict):
result['msg'] = event
result['type'] = 'dict'
result['say'] = 'hello world'
else:
result['msg'] = event.decode("utf-8")
result['type'] = 'non-dict'
result['say'] = 'hello world'
return result
Publish a dict format message:
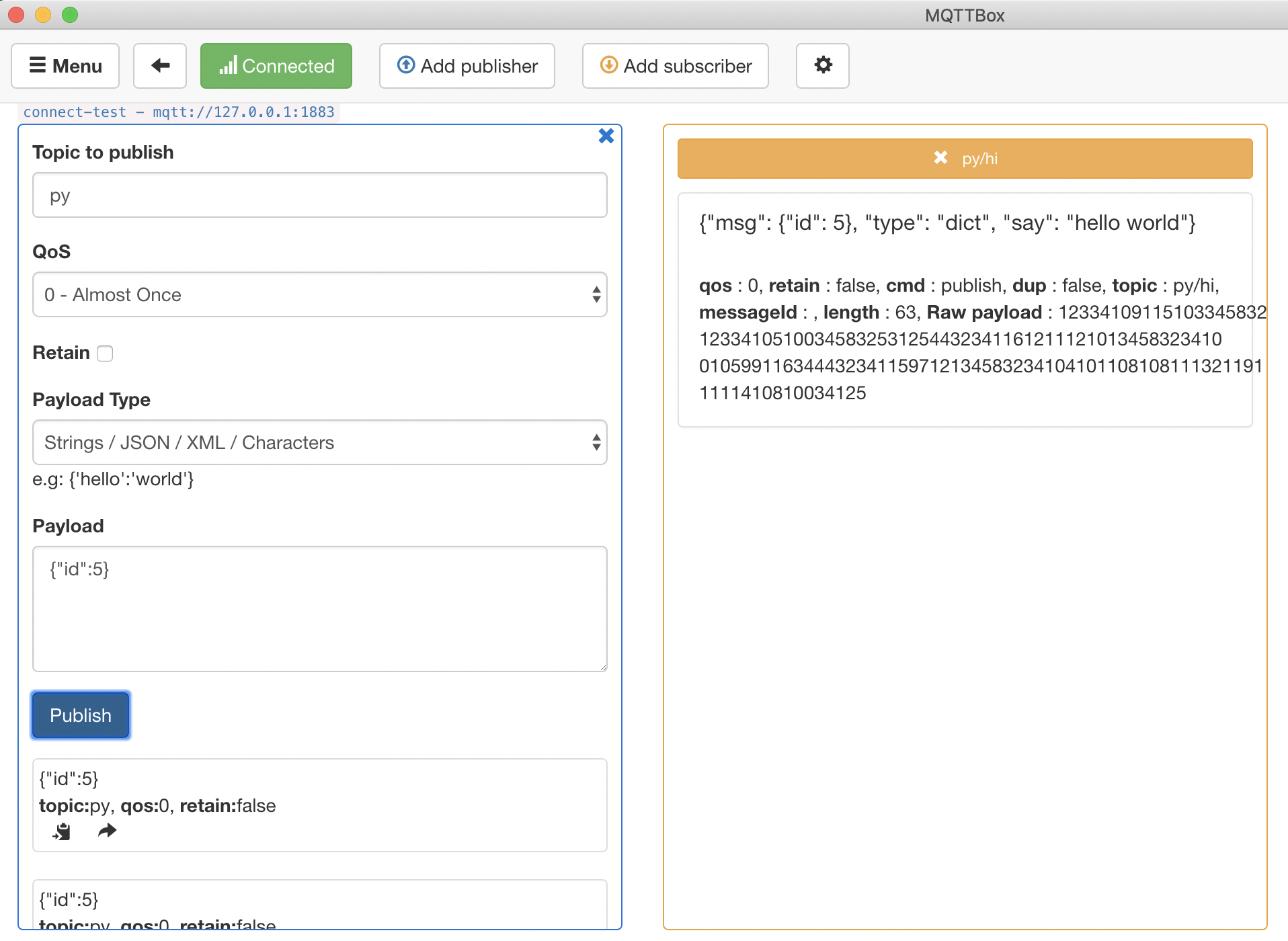 Publish a dict format message
Publish a dict format message
Publish an non-dict format message:
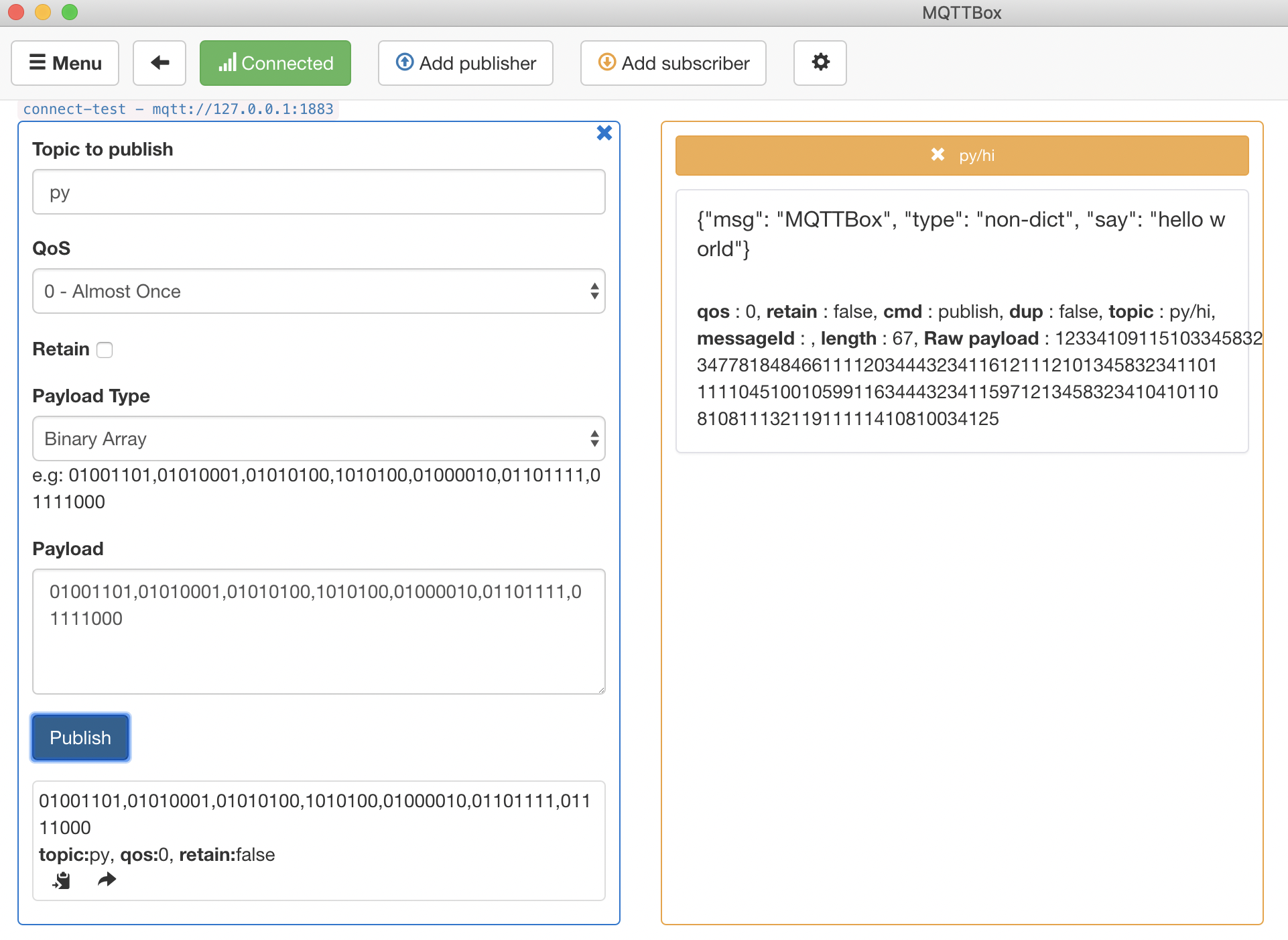 Publish an non-dict format message
Publish an non-dict format message
As above, for some general needs, we can implement it through the Python Standard Library. However, for some more complex demands, it is often necessary to import third-party libraries to complete. How to solve the problem? We’ve provided a general solution in How to import third-party libraries for Python runtime.